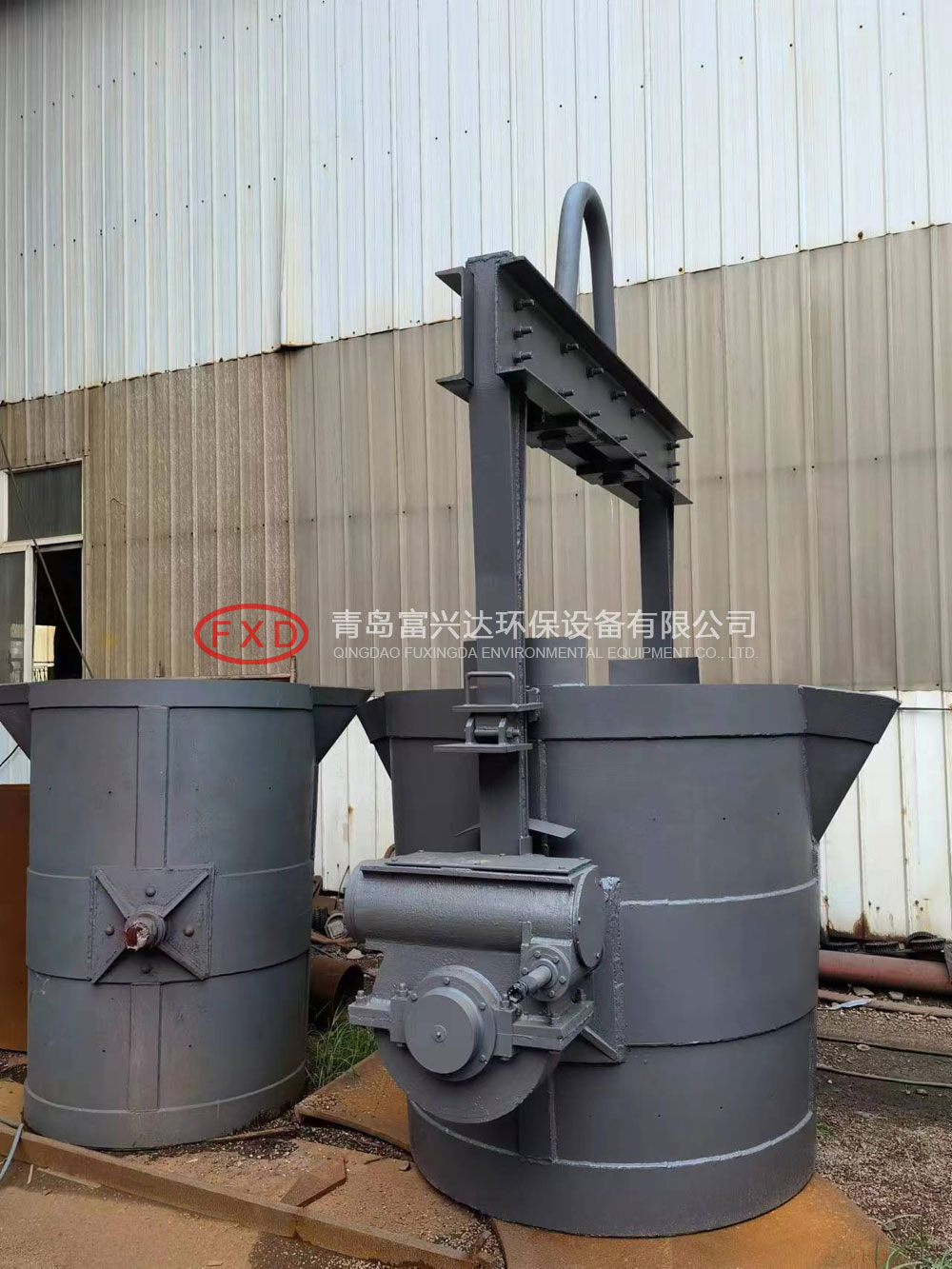
The problems existing in the use of molten iron ladle mainly include the following aspects:
1. The number of minor repairs of molten iron ladle is large, and the turnover is difficult. The molten iron ladle after minor repair needs to be maintained for 8h, and then baked for 8h before it can be put into use. The long maintenance time increases the turnover difficulty of the molten iron ladle
2. Uneven erosion of wall bricks
In order to ensure the safety of the molten iron ladle during use, the residual thickness of wall bricks after the ladle is offline is required to be greater than 60mm. Uneven erosion of wall-clad bricks and local residual thickness too small (less than 50mm) occur during use. This limits the further improvement of ladle service life
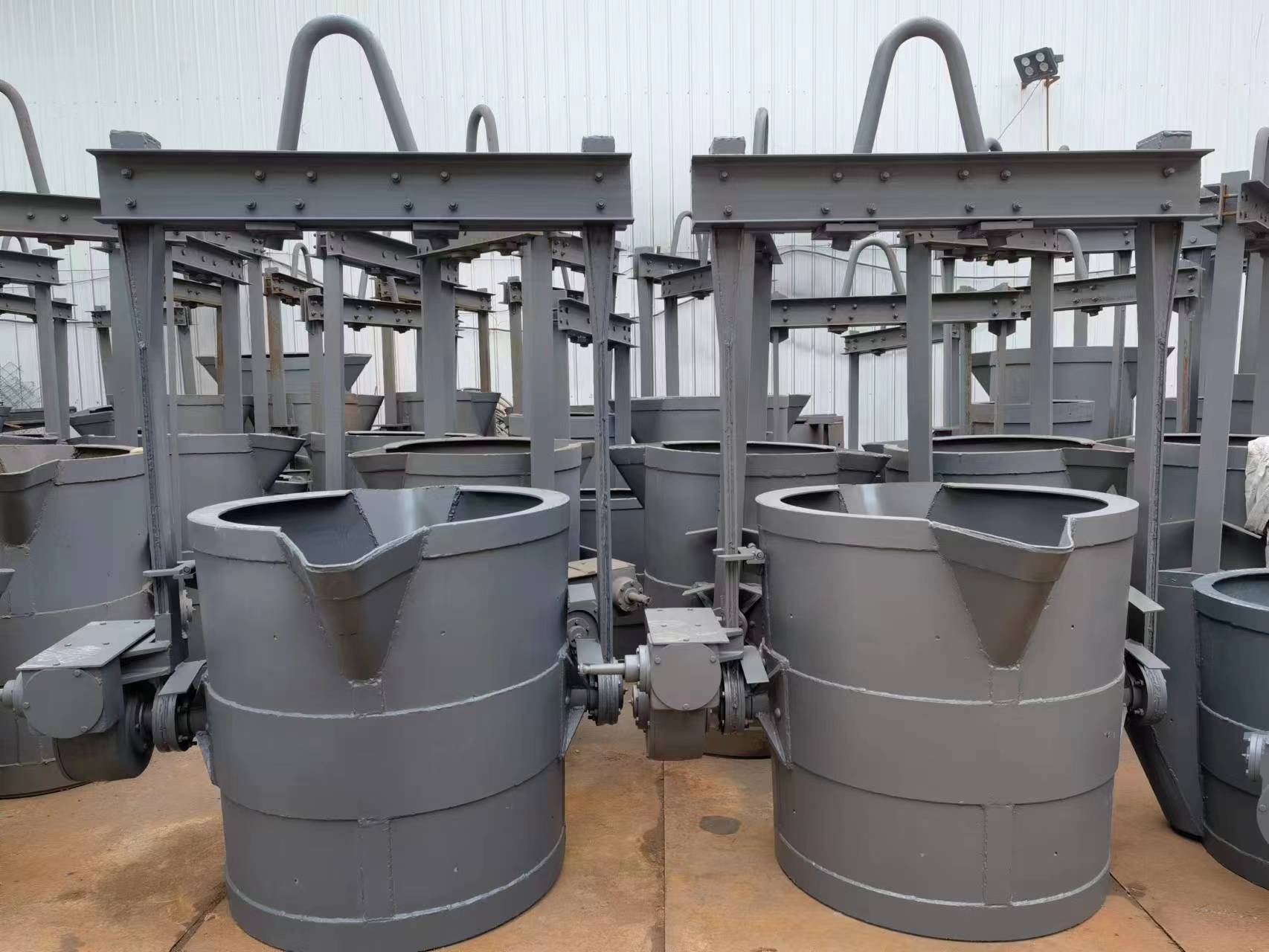

molten iron ladle
3. Slag sticking and brick dropping at the ladle nozzle are serious
The process of slag sticking at the ladle nozzle is that the ladle nozzle brick is eroded by molten iron during use, resulting in loose ladle nozzle brick and increased gap; The molten iron slag penetrates into the brick along the hole of the ladle mouth brick, the high-temperature slag and the brick body have physical and chemical reaction, and the slag and the lining brick penetrate each other and interpenetrate with each other, which makes the slag and the brick combine very firmly and difficult to remove and form sticky slag
After slag sticking at the nozzle, the original nozzle shape is damaged, resulting in iron sprinkling at the nozzle during iron loading. Generally, the treatment method is to clear the slag sticking at the nozzle online. Slag and iron sticking at the ladle nozzle are not only difficult to deal with, but also often cause the fall-off of refractory materials at the ladle nozzle. When the ladle is turned around again, the molten iron washes the ladle nozzle steel shell, seriously affecting the service life of the ladle. The main reason for the frequent drop-off of molten iron ladle is that the ladle nozzle is sprayed with iron due to the slag sticking on the ladle nozzle
4. The corrosion resistance of the bottom of the molten iron ladle is poor.
The corrosion of the refractory material is divided into physical erosion and chemical erosion. Physical erosion refers to the erosion of the refractory material by impact and other mechanical actions; Chemical erosion refers to the erosion of refractory materials by the change of temperature field and stress field under the action of high temperature load. The bottom of molten iron ladle is mainly physical erosion. During the use of molten iron ladle, the castable of the working layer at the bottom of the ladle has poor corrosion resistance and impact resistance. Under the impact and erosion of high temperature molten iron, a large area of refractory material falls off, with the delamination thickness of 100mm~150mm, and the delamination parts are mostly concentrated on the side of the buckle. This brings great hidden danger to the safe use of molten iron ladle


 111
111